How to build an accessible search bar component in React
A search bar is a great way to make content on your website discoverable. In this tutorial, we’ll be building an search bar component using React JS. I’ll also be covering some accessibility concerns you should keep in mind. And finally, we’ll be adding a couple of unit tests with React Testing Library.
Here’s our final product:
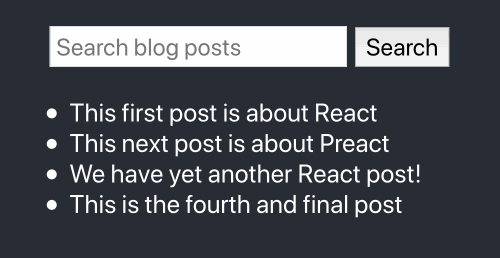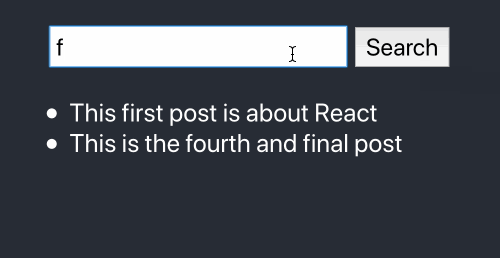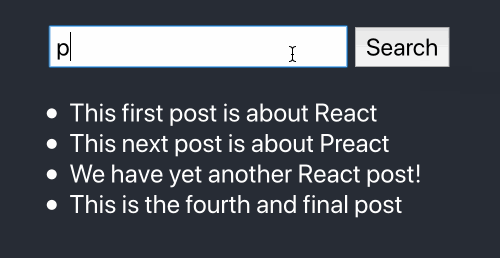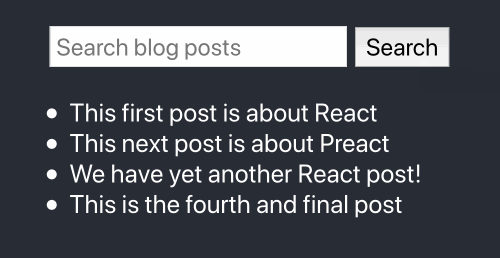
If you want to jump straight to a code example, the source code for this tutorial is available at react-search-bar.
Render your search bar component in the app
To get started, create a new file for your search component. I’ve called mine search.js:
const Search = () => {
return <div>Hello world!</div>
}
export default Search;And then render this component from inside of your main app file:
import Search from './search';
const App = () => {
return (
<Search />
);
}
export default App;Add your HTML elements
Our search bar component will contain a couple of HTML elements. Add a label, input and button, and then wrap it all in a form element:
const SearchBar = () => (
<form action="/" method="get">
<label htmlFor="header-search">
<span className="visually-hidden">Search blog posts</span>
</label>
<input
type="text"
id="header-search"
placeholder="Search blog posts"
name="s"
/>
<button type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
);
export default SearchBar;This will render like this:
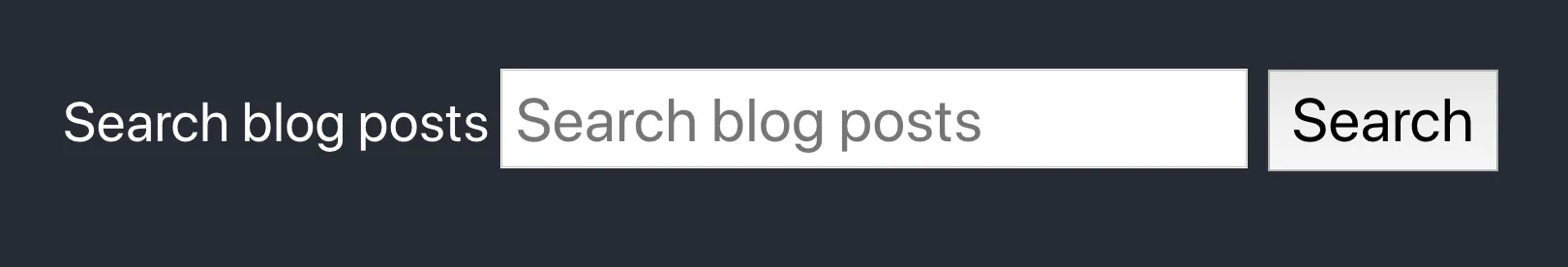
Accessibility and labels
You might be wondering why we are doubling up on the label and placeholder text.
This is because placeholders aren’t accessible. By adding a label, we can tell screen reader users what the input field is for. We can hide our label using a visually-hidden CSS class:
.visually-hidden {
clip: rect(0 0 0 0);
clip-path: inset(50%);
height: 1px;
overflow: hidden;
position: absolute;
white-space: nowrap;
width: 1px;
}This keeps it visible to screen reader users, but invisible to everyone else.
Now we have a functioning search bar! When you search, you will navigate to /?s=<your_query_here>.

Add a list of posts
Now that we can search, we’ll need a list of items to search from. I’ve created a list of fake posts:
const posts = [
{ id: '1', name: 'This first post is about React' },
{ id: '2', name: 'This next post is about Preact' },
{ id: '3', name: 'We have yet another React post!' },
{ id: '4', name: 'This is the fourth and final post' },
];Use the map function to loop through and render them:
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<Search />
<ul>
{posts.map((post) => (
<li key={post.id}>{post.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}Filter the list based on your search query
Our search bar will navigate us to a new URL when we perform a search. We can grab this value from the URL:
const { search } = window.location;
const query = new URLSearchParams(search).get('s');We’ll also need a function that filters out posts depending on the search query. If the list you’re querying over is simple, you can write your own:
const filterPosts = (posts, query) => {
if (!query) {
return posts;
}
return posts.filter((post) => {
const postName = post.name.toLowerCase();
return postName.includes(query);
});
};You can also rely on third-party search libraries like js-search to filter posts for you.
Using your search query and filter function, you can render the posts that match your search:
const App = () => {
const { search } = window.location;
const query = new URLSearchParams(search).get('s');
const filteredPosts = filterPosts(posts, query);
return (
<div>
<Search />
<ul>
{filteredPosts.map(post => (
<li key={post.key}>{post.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}Now when you type in a query, you will be able to filter your posts!
Adding immediate search or “search as you type”
Instead of pressing enter to submit your search, you may also want the list to filter as the user begins typing. This immediate response can be more pleasant from a user-experience perspective.
To add this feature, you can store a searchQuery value in your component’s state, and change this value as the user begins typing:
import { useState } from 'react';
function App() {
const { search } = window.location;
const query = new URLSearchParams(search).get('s');
const [searchQuery, setSearchQuery] = useState(query || '');
const filteredPosts = filterPosts(posts, searchQuery);
return (
<div>
<Search
searchQuery={searchQuery}
setSearchQuery={setSearchQuery}
/>
<ul>
{filteredPosts.map(post => (
<li key={post.key}>{post.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}After you pass in the searchQuery and setSearchQuery props, you’ll need to make use of it in your input element:
const SearchBar = ({ searchQuery, setSearchQuery }) => (
<form action="/" method="get">
<label htmlFor="header-search">
<span className="visually-hidden">Search blog posts</span>
</label>
<input
value={searchQuery}
onInput={e => setSearchQuery(e.target.value)}
type="text"
id="header-search"
placeholder="Search blog posts"
name="s"
/>
<button type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
);Now, as soon as you start typing, your posts will begin filtering!

Adding SPA navigation with React Router
Currently your search bar will do a full-page refresh when you press enter. If you’re looking to build a single-page app (SPA), you’ll want to use a routing library like React Router. You can install it with the following command:
yarn add react-router-domAfter installing it, wrap your app in the Router component:
import { BrowserRouter as Router } from "react-router-dom";
const App = () => {
return <Router>
{ /* ... */ }
</Router>
}And then add the following to the top of your search component:
import { useHistory } from 'react-router-dom';
const SearchBar = ({ searchQuery, setSearchQuery }) => {
const history = useHistory();
const onSubmit = e => {
history.push(`?s=${searchQuery}`)
e.preventDefault()
};
return <form action="/" method="get" autoComplete="off" onSubmit={onSubmit}>Now when a user presses enter, the app’s URL will change without a full-page refresh.
“Search as you type”, SPA navigation and accessibility concerns
Without a full-page refresh, you won’t be notifying screen reader users if the items in the list change. We can send these notifications using ARIA live regions.
After some Googling, there are packages like react-aria-live and react-a11y-announcer that will help you do this. Unfortunately, it seems like neither of these have been updated in over a year.
Luckily, it is simple to write your own announcer component:
const Announcer = ({ message }) =>
<div role="region" aria-live="polite" className="visually-hidden">{message}</div>
export default Announcer;And then render this in your main app component:
<Announcer message={`List has ${filteredPosts.length} posts`}/>Whenever the message changes in your Announcer component, screen readers will read out the message.
Now, as you search, screen reader users will receive an update letting them know how many posts are on the page.
This isn’t a perfect solution, but it’s much better than having your items silently change.
If you are on a Mac and testing its VoiceOver feature, make sure to use Safari! I find that other browsers don’t work as well with screen readers.
Testing your component with React Testing Library
To wrap things up, we’ll be testing our component using React Testing Library. This library comes out of the box with create-react-app.
The first test we’ll be adding is an accessibility check using axe. To use it, add the jest-axe package to your repository:
yarn add jest-axeWe can use axe to test that our search component does not have any accessibility violations:
import { render } from '@testing-library/react';
import { axe, toHaveNoViolations } from 'jest-axe';
import Search from '../src/search';
expect.extend(toHaveNoViolations);
test('should not have any accessibility violations', async () => {
const { container } = render(<Search searchQuery='' />);
const results = await axe(container);
expect(results).toHaveNoViolations();
});
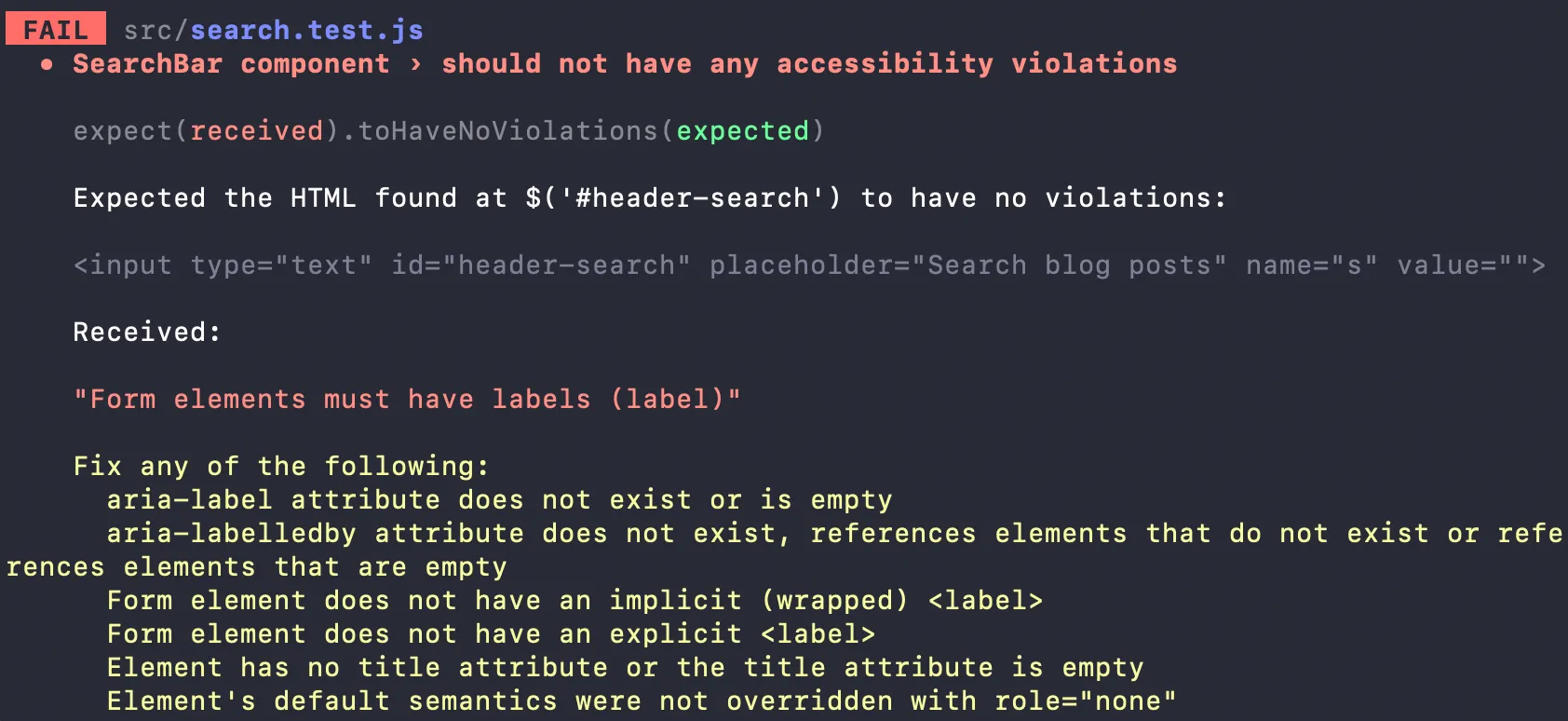
We should also add a test for the functionality of your component. Let’s add one that tests that when you type “preact”, it only shows one post:
test('should render one post when user searches for preact', () => {
render(<App />);
let posts = screen.getAllByRole('listitem');
expect(posts.length).toEqual(4);
const searchBar = screen.getByRole('textbox');
userEvent.type(searchBar, 'preact');
posts = screen.getAllByRole('listitem');
expect(posts.length).toEqual(1);
});
Conclusion
After reading this tutorial, you will be able to create an accessible search bar component for your React app. With unit tests! You can see the full source code at react-search-bar.